Featured
How To Calculate Pi With 3 Pka Values
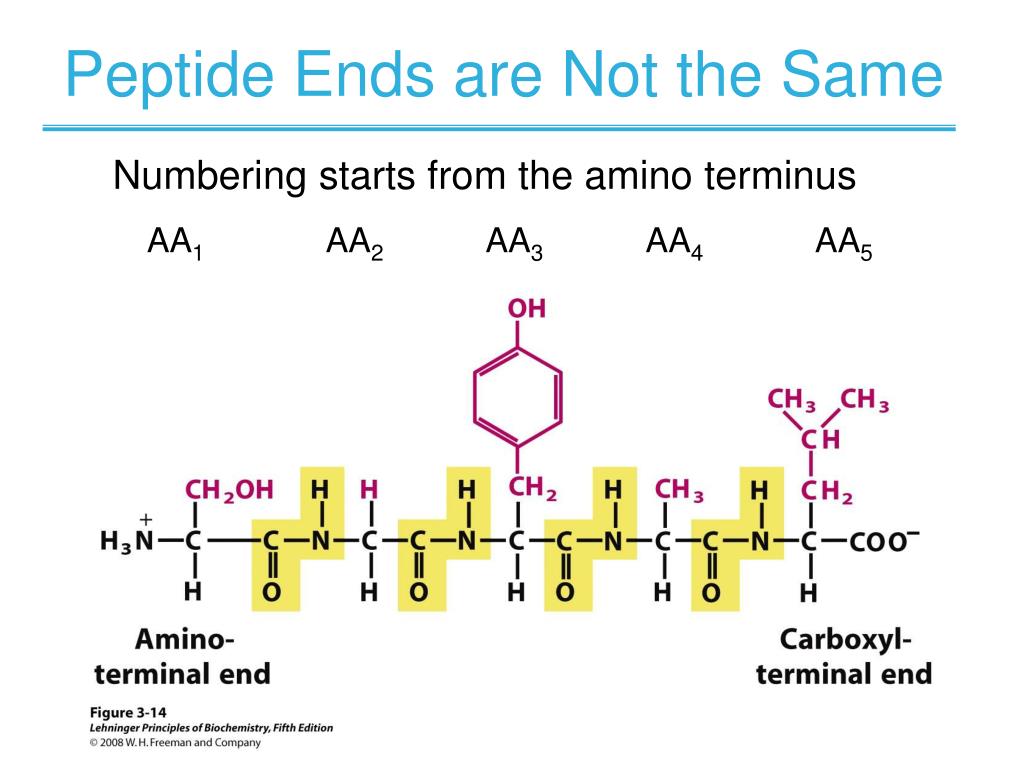
How To Calculate Pi With 3 Pka Values. Make up an approx 0.1m solution of the acid. For this we should refer to the titration curve of the amino acid.
The sum of charges on the basic and the acidic groups gives the net charge on the molecule at the specified ph. It is somewhat similar to the previous method and also one of the conventional methods. This video shows you how to calculate amino acid isoelectric.
This Video Shows You How To Calculate Amino Acid Isoelectric.
If we set the amount of protonated acid, ha, to 1, then by the equation. Let’s apply this equation to glycine. It is somewhat similar to the previous method and also one of the conventional methods.
Since The P I Is The P H At Which The Amino Acid Has No Overall Net Charge, You Need To Average The P K A Values Relevant To The.
The pka1 of the carboxylic. This comes from a balance of protonation and deprotonation so that all positive and negative charges cancel out. Pka is associated with a weak acid.
Pi) Is The Ph At Which The Amino Acid Has A Net Zero Charge.
Technically it's the average of the two pka's that surround the neutral zwitterion. Isoelectric point (pi) can be calculated using the formula, pi = pka1 + pka2/ 2 for molecules with two ionizable groups (e.g. The isoelectric point (isoelectric ph;
For This We Should Refer To The Titration Curve Of The Amino Acid.
Calculating pi is relatively simple, especially when there are only two groups with pka values. (nh3) 10 > 3 = +. This is what it looks like.
The Equation Is Simply This:
The “p” in ph, pka, and pi denotes the negative logarithm, to base 10, of the parameter in question. A lower pka value indicates a stronger acid. To get the proportion of acid a that is protonated, we need to calculate the ratio of protonated acid to all acid species.
Comments
Post a Comment