Featured
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Variance Of The Probability Distribution Calculator
Variance Of The Probability Distribution Calculator. Simply fill in the cells below for up to 10 values, then click the. Simply enter your data into the textbox below, either one score per line or as a comma delimited list, and then.
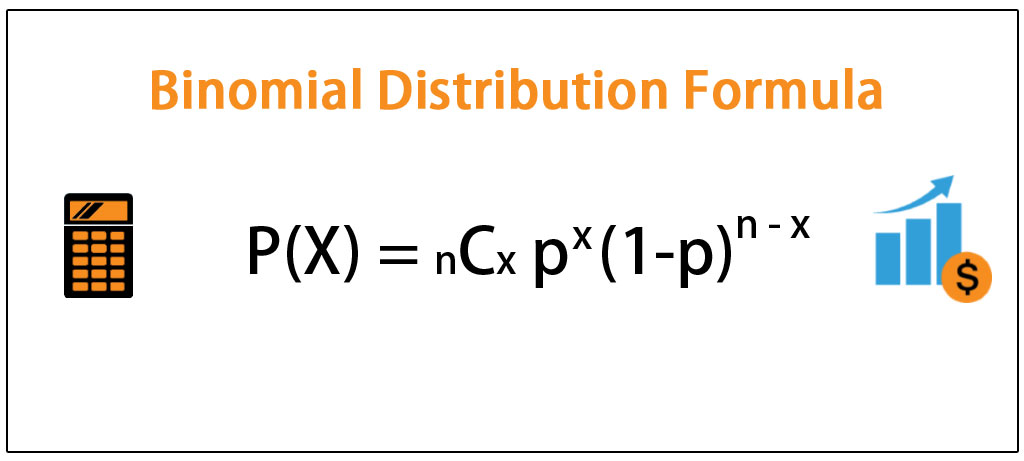
Mean or expected value, variance, and standard deviation. First, determine the values of the two parameters that are required to define a binomial distribution: This sequence of events fulfills the prerequisites of a binomial distribution.
P (X < A) Step 5.
P (x) = e^ {−λ}λ^x / x! Variance calculator probability helps to determine the variance of random variable x of discrete probability distribution & probability density function (pdf). Binomial probability function f ( x) = ( n x) p x ( 1 − p) ( n − x) ( n x) = n!
S S = ∑ I = 1 N ( X I − X ¯) 2.
This simple tool will calculate the variance of a set of data. So, you subtract each value from the mean of the collection and square the result. This is a measure of dependence between x and y.
We Can Say That On Average If We.
This calculator automatically finds the mean, standard deviation, and variance for any probability distribution. E ( x) variance of x: You can find the variance using the following formula:
Var (X+Y) = Var (X) + Var (Y) + Cov (X,Y).
Then you add all these. Bivariate standard n ormal distribution (1)probability density f(x,y,ρ)= 1 2π√1−ρ2 e− x2−2ρxy+y2 2(1−ρ2) (2)upper cumulative distribution q(x,y,ρ) =∫ ∞ x ∫∞ y f(u1,u2,ρ)du1du2 b i v a r i a t e s t a. This sequence of events fulfills the prerequisites of a binomial distribution.
Variance = Σ 2 = Σ ( X I − Μ).
Var (x + a) = var (x) for any scalar a. How to use the normal distribution and probability calculator to use our calculator, you must do the following: Mean or expected value of discrete random.
Comments
Post a Comment